
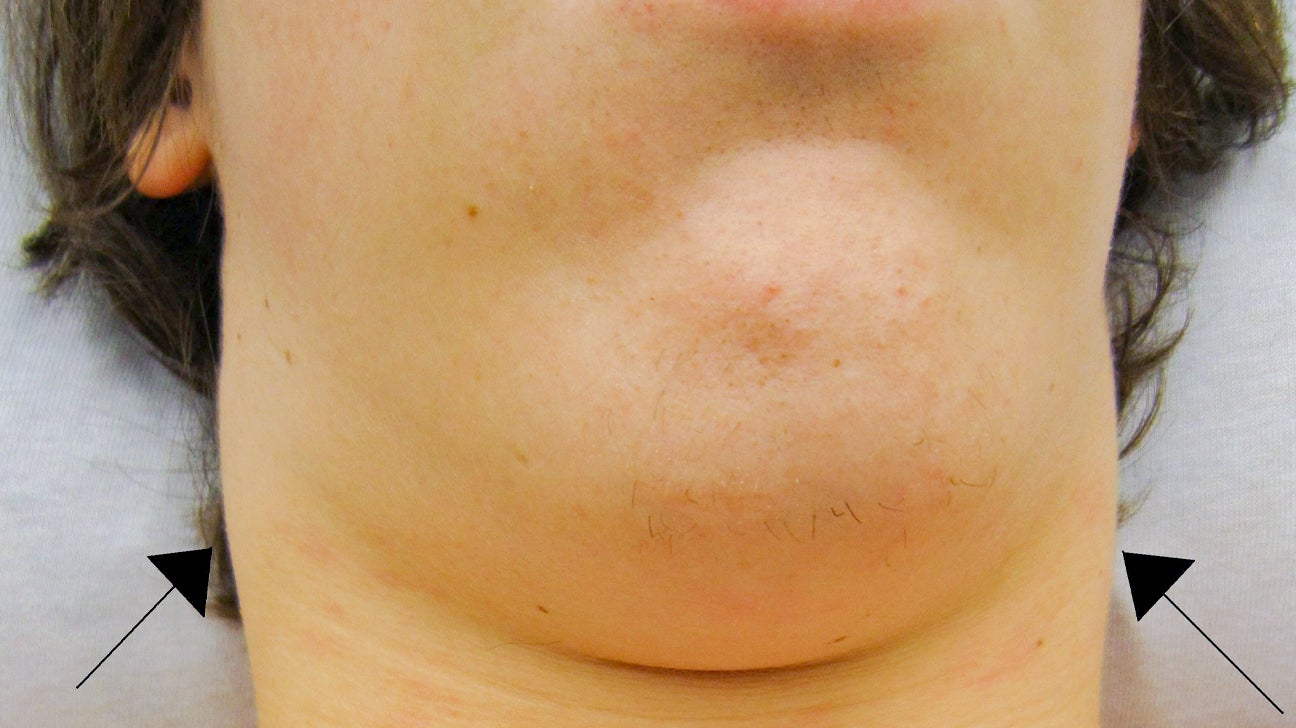
Swollen glands may accompany a sore throat - which can cause painful swallowing and may feel like there is a soreness, discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat - depending on the cause of the pain. The lump may or may not be tender or painful, and you may feel one lump or several. Some swollen lymph nodes are only slightly noticeable. RELATED: What Does Arthritis Pain Feel Like?Ī lump that you see or feel, especially in your neck, armpit, or groin, can be a symptom of lymphadenopathy. Sometimes the swelling is localized (in only one place in the body), and sometimes it's diffuse (throughout the body). When lymph nodes become swollen or enlarged, doctors refer to the condition as lymphadenopathy. In a nutshell, lymph nodes help keep you healthy. Lymph nodes (also known as glands) filter waste out of lymph, a sticky, clear fluid that contains white blood cells, which help fight infection. This is especially true in children, whose glands may decrease in size while remaining firm and visible for many weeks.You have hundreds of lymph nodes throughout your body, and large clusters of them in three particular areas: your neck, your armpits, and your groin. Lymph nodes may remain swollen or firm long after an initial infection is gone. How long will lymph nodes remain swollen? If cancer is suspected, a biopsy may be done to confirm the diagnosis.Īny swollen lymph nodes that don't go away or return to normal size within about a month should be checked by your doctor. For example, a bacterial infection may be treated with antibiotics, while a viral infection often goes away on its own. Treatment for swollen glands focuses on treating the cause. Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection.This virus attacks the immune system, making it difficult for the body to fight off infection and some disease. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which develops after a person contracts HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).Cancer, such as leukemia, Hodgkin disease, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Side effects of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccination.Side effects of phenytoin (Dilantin), a medicine used to prevent seizures.A bacterial illness, such as strep throat (caused by the streptococcus bacterium) or Lyme disease (a bacterial infection spread by certain types of ticks).Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus), which results in fever, sore throat, and fatigue, or cytomegalovirus (CMV), a viral infection that causes symptoms similar to those of mononucleosis.A viral illness, such as measles, rubella, chickenpox (varicella), or mumps.When lymph nodes swell in two or more areas of the body, it is called generalized lymphadenopathy. Glands above the collarbone (supraclavicular lymph nodes) may swell from an infection or tumour in the areas of the lungs, breasts, neck, or abdomen.Ĭommon sites for swollen lymph nodes include the neck, groin, and underarms.In rare cases, testicular cancer, lymphoma, or melanoma may cause a lump in this area. The lymph nodes in the groin (femoral or inguinal lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection in the foot, leg, groin, or genitals.A rare cause of axillary swelling may be breast cancer or lymphoma. Glands in the armpit (axillary lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection to the arm or hand.Glands can also swell following an injury, such as a cut or bite, near the gland or when a tumour or infection occurs in the mouth, head, or neck. The glands on either side of the neck, under the jaw, or behind the ears commonly swell when you have a cold or sore throat.Which lymph nodes are swollen can help identify the problem.

Lymph nodes often swell in one location when a problem such as an injury, infection, or tumour develops in or near the lymph node. Most lymph nodes in the body cannot be felt.

Lymph nodes generally are not tender or painful. Groups of lymph nodes can be felt in the neck, groin, and underarms.
And they may be as small as the head of a pin or as large as an olive. Lymph nodes may be found singly or in groups. The lymph nodes filter lymph fluid as it flows through them, trapping bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances, which are then destroyed by special white blood cells called lymphocytes. The lymph system is an important part of the immune system, the body's defence system against disease. They are part of the lymph system, which carries fluid (lymph fluid), nutrients, and waste material between the body tissues and the bloodstream. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands throughout the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
